Subtitle: Predict Secretory Protein in microbes with SignalP and TMHMM
分泌蛋白是指在细胞内合成后,分泌到细胞外起作用的蛋白质。分泌蛋白的 N 端有一般由 15~30 个氨基酸组成的信号肽。信号肽是引导新合成的蛋白质向分泌通路转移的短(长度 5-30 个氨基酸)肽链。常指新合成多肽链中用于指导蛋白质的跨膜转移(定位)的 N - 末端的氨基酸序列(有时不一定在 N 端)。使用 SignalP 注释蛋白序列是否含有信号肽结构,使用 TMHMM 注释蛋白序列是否含有跨膜结构,最终筛选出含有信号肽结构并且不含跨膜结构的蛋白为分泌蛋白。
#软件
SignalP V6.0
SignalP 6.0预测来自古细菌、革兰氏阳性细菌、革兰氏阴性细菌和真核生物的蛋白质中存在的信号肽及其切割位点的位置。在细菌和古细菌中,SignalP 6.0 可以区分五种类型的信号肽:
Sec/SPI:由 Sec 转座转运,并由信号肽酶 I (Lep) 切割的 “标准” 分泌信号肽;
Sec/SPII:由 Sec 转座子运输,并由信号肽酶 II (Lsp) 切割的脂蛋白信号肽;
Tat/SPI:由 Tat 转座子转运,并由信号肽酶 I (Lep) 切割的 Tat 信号肽;
Tat/SPII:由 Tat 转位子转运,并由信号肽酶 II (Lsp) 切割的 Tat 脂蛋白信号肽;
Sec/SPIII:由 Sec 转位子运输,并由信号肽酶 III (PilD/PibD) 切割的菌毛蛋白和菌毛蛋白样信号肽。
此外,SignalP 6.0 预测信号肽的区域。根据类型,预测 n、h 和 c 区域以及其他显着特征的位置。
TMHMM V2.0c
- 用于预测蛋白质中的跨膜螺旋。
Python
SignalP 和 TMHMM 对于学术用户免费,但是需要填写相关信息和邮箱,以接收下载链接(4h 有效时间)。
#软件安装
# 安装 SignalP 6.0
下载
访问 SignalP V6.0 网站,找到 “Download”,填写相关信息,获取下载链接,下载得到 “signalp-6.0.fast.tar.gz”。有两个模式可以选择 ——“slow_sequential” 和 “fast"。前者 runs the full model sequentially, taking the same amount of RAM as
fastbut being 6 times slower;后者 uses a smaller model that approximates the performance of the full model, requiring a fraction of the resources and being significantly faste。本教程下载的是 fast 模式。安装
安装依赖
Python
matplotlib>3.3.2
numpy>1.19.2
torch>1.7.0
pip install torchtqdm>4.46.1
安装 SignalP 6.0
# 解压缩安装文件tar zxvf signalp-6.0.fast.tar.gz# 进入解压后的软件目录,在终端运行python setup.py install# 测试安装signalp6 --help
# 安装 TMHMM V2.0c
下载
访问 TMHMM V2.0c 网站,找到 “Download”,填写相关信息,获取下载链接,下载得到 “tmhmm-2.0c.Linux.tar.gz”。
安装
# 解压缩tar zxvf tmhmm-2.0c.Linux.tar.gz# 进入解压后的目录cd tmhmm-2.0c# 获取当前路径,我的是 “/home/liu/tools/tmhmm-2.0c/bin”pwd# 将该路径加入到系统的环境变量中,参考我之前的文章来(编辑~/.bashrc)https://liaochenlanruo.github.io/post/f6c9.html#% E6% B7% BB% E5%8A% A0% E7%8E% AF% E5% A2%83% E5%8F%98% E9%87%8F# 修改 bin 目录下的 tmhmm 和 tmhmmformat.pl 的首行为 “#!/usr/bin/perl”运行错误
运行软件时总报
Segmentation fault (core dumped)错误,暂时无解。各位可以使用其在线版。
#软件用法
# SignalP 6.0
#预测
A command takes the following form
signalp6 --fastafile /path/to/input.fasta --organism other --output_dir path/to/be/saved --format txt --mode fast |
fastafile输入文件为 FASTA 格式的蛋白序列文件。organismis eitherotherorEukarya. SpecifyingEukaryatriggers post-processing of the SP predictions to prevent spurious results (only predicts type Sec/SPI).formatcan take the valuestxt,png,eps,all. It defines what output files are created for individual sequences.txtproduces a tabular.gfffile with the per-position predictions for each sequence.png,eps,alladditionally produce probability plots in the requested format. For larger prediction jobs, plotting will slow down the processing speed significantly.modeis eitherfast,sloworslow-sequential. Default isfast, which uses a smaller model that approximates the performance of the full model, requiring a fraction of the resources and being significantly faster.slowruns the full model in parallel, which requires more than 14GB of RAM to be available.slow-sequentialruns the full model sequentially, taking the same amount of RAM asfastbut being 6 times slower. If the specified model is not installed, SignalP will abort with an error.
#输出
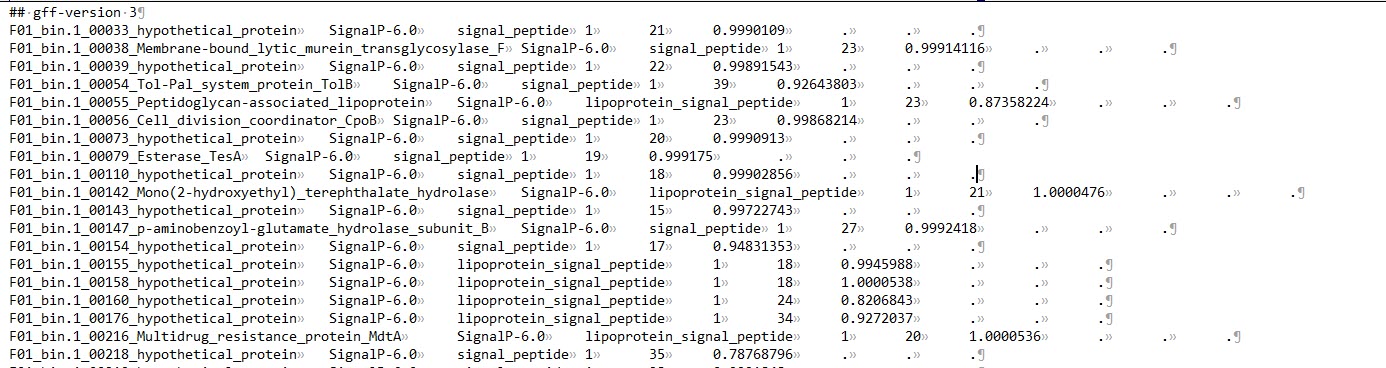
output_dir/output.gff3:仅包含含有信号肽的序列信息;
![output.gff3]()
output_dir/prediction_results.txt:包含了输入文件中的所有序列(不重要);
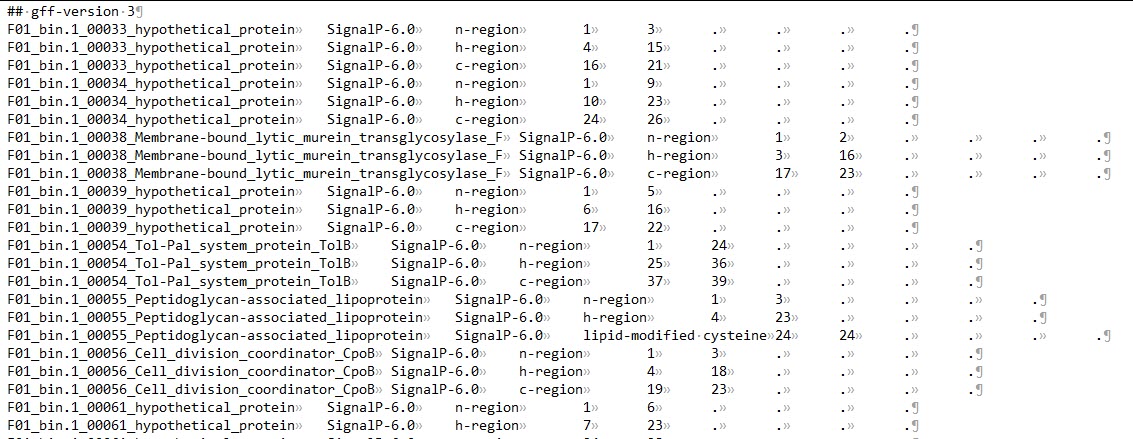
output_dir/region_output.gff3:包含所有的信号肽区域信息。
n-region: The n-terminal region of the signal peptide. Reported for Sec/SPI, Sec/SPII, Tat/SPI and Tat/SPII. Labeled as N
h-region: The center hydrophobic region of the signal peptide. Reported for Sec/SPI, Sec/SPII, Tat/SPI and Tat/SPII. Labeled as H
c-region: The c-terminal region of the signal peptide, reported for Sec/SPI and Tat/SPI.
Cysteine: The conserved cysteine in +1 of the cleavage site of Lipoproteins that is used for Lipidation. Labeled as c.
Twin-arginine motif: The twin-arginine motif at the end of the n-region that is characteristic for Tat signal peptides. Labeled as R.
Sec/SPIII: These signal peptides have no known region structure.
![region_output.gff3]()
# 批处理与结果优化
脚本名:run_SignalP.pl
#!/usr/bin/perl | |
use strict; | |
use warnings; | |
# Author: Liu Hualin | |
# Date: Oct 14, 2021 | |
open IDNOSEQ, ">IDNOSEQ.txt" || die; | |
my @faa = glob("*.faa"); | |
foreach (@faa) { | |
$_ =~ /(.+).faa/; | |
my $str = $1; | |
my $out = $1 . ".nodesc"; | |
my $sigseq = $1 . ".sigseq"; | |
my $outdir = $1 . "_signalp"; | |
open IN, $_ || die; | |
open OUT, ">$out" || die; | |
while (<IN>) { | |
chomp; | |
if (/^(>\S+)/) { | |
print OUT $1 . "\n"; | |
}else { | |
print OUT $_ . "\n"; | |
} | |
} | |
close IN; | |
close OUT; | |
my %hash = idseq($out); | |
system("signalp6 --fastafile $out --organism other --output_dir $outdir --format txt --mode fast"); | |
my $gff = $outdir . "/output.gff3"; | |
if (! -z $gff) { | |
open IN, "$gff" || die; | |
<IN>; | |
open OUT, ">$sigseq" || die; | |
while (<IN>) { | |
chomp; | |
my @lines = split /\t/; | |
if (exists $hash{$lines[0]}) { | |
print OUT ">$lines[0]\n$hash{$lines[0]}\n"; | |
}else { | |
print IDNOSEQ $str . "\t" . "$lines[0]\n"; | |
} | |
} | |
close IN; | |
close OUT; | |
} | |
system("rm $out"); | |
system("mv $sigseq $outdir"); | |
} | |
close IDNOSEQ; | |
sub idseq { | |
my ($fasta) = @_; | |
my %hash; | |
local $/ = ">"; | |
open IN, $fasta || die; | |
<IN>; | |
while (<IN>) { | |
chomp; | |
my ($header, $seq) = split (/\n/, $_, 2); | |
$header =~ /(\S+)/; | |
my $id = $1; | |
$hash{$id} = $seq; | |
} | |
close IN; | |
return (%hash); | |
} |
将 run_SignalP.pl 与后缀名为 “.faa” 的 FASTA 格式文件放在同一目录下,在终端中运行如下代码:
perl run_SignalP.pl |
#结果解读
* 代表输入文件的名字。
*_signalp/output.gff3:仅包含含有信号肽的序列信息;
*_signalp/prediction_results.txt:包含了输入文件中的所有序列(不重要);
*_signalp/region_output.gff3:包含所有的信号肽区域信息;
*_signalp/*.sigseq:存储所有信号肽的氨基酸序列文件,可用作 TMHMM 的输入文件。
# TMHMM
# 预测
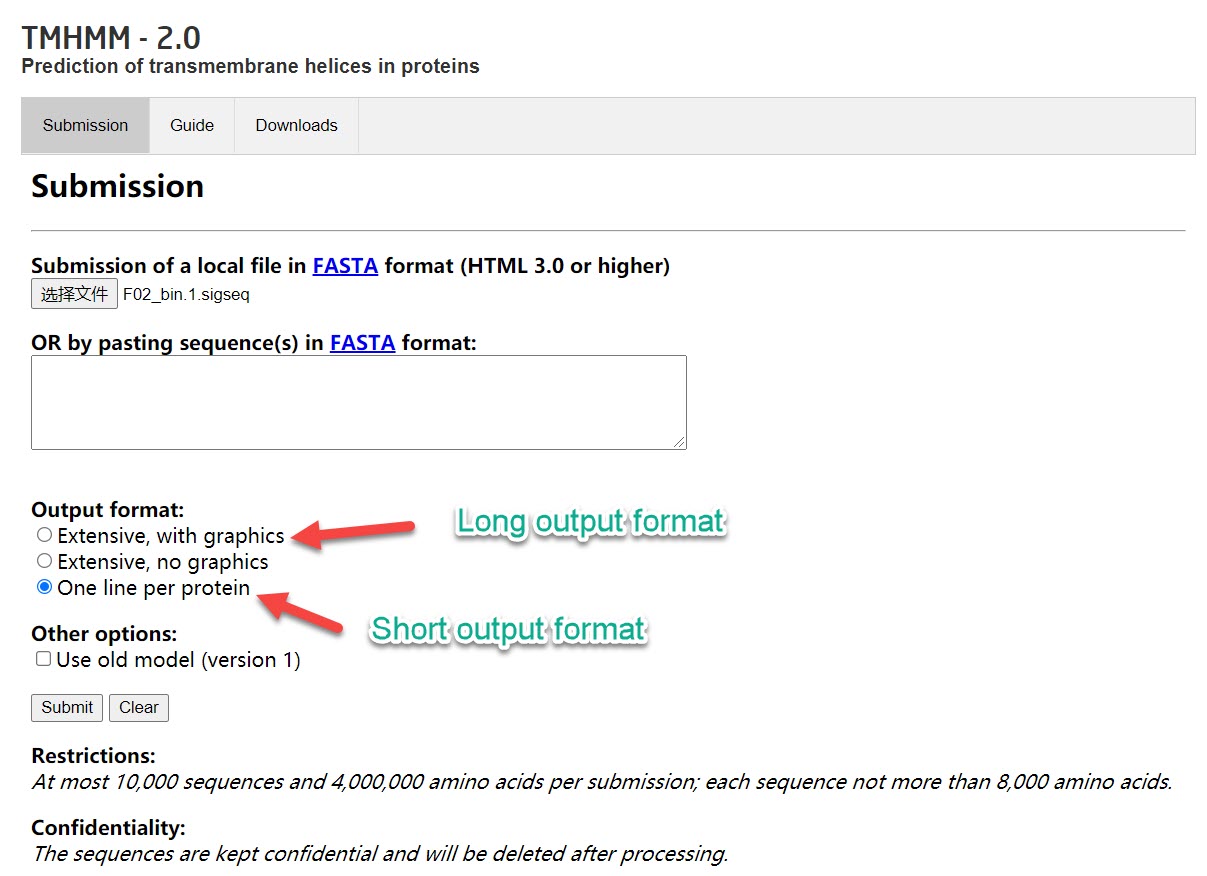
离线版总是报错,找不出原因,因此使用网页服务器进行,输入文件为上述生成的 “*_signalp/*.sigseq”,将其上传至网页版 TMHMM,提交任务,等待结果即可。
# 结果展示
TMHMM 可以输出多种格式的结果文件,具体请参考其官方说明。
Long output format
Length:蛋白序列的长度。
Number of predicted TMHs:预测到的跨膜螺旋的数量。
Exp number of AAs in TMHs:跨膜螺旋中氨基酸的预期数量。如果此数字大于 18,则很可能是跨膜蛋白(或具有信号肽)。
Exp number, first 60 AAs:在蛋白的前 60 个氨基酸中跨膜螺旋中氨基酸的预期数量。如果该数字超过几个,你应该被警告在 N 端预测的跨膜螺旋可能是一个信号肽。
Total prob of N-in:N 端在膜的细胞质一侧的总概率。
POSSIBLE N-term signal sequence:当 “Exp number, first 60 AAs” 大于 10 时产生的警告。
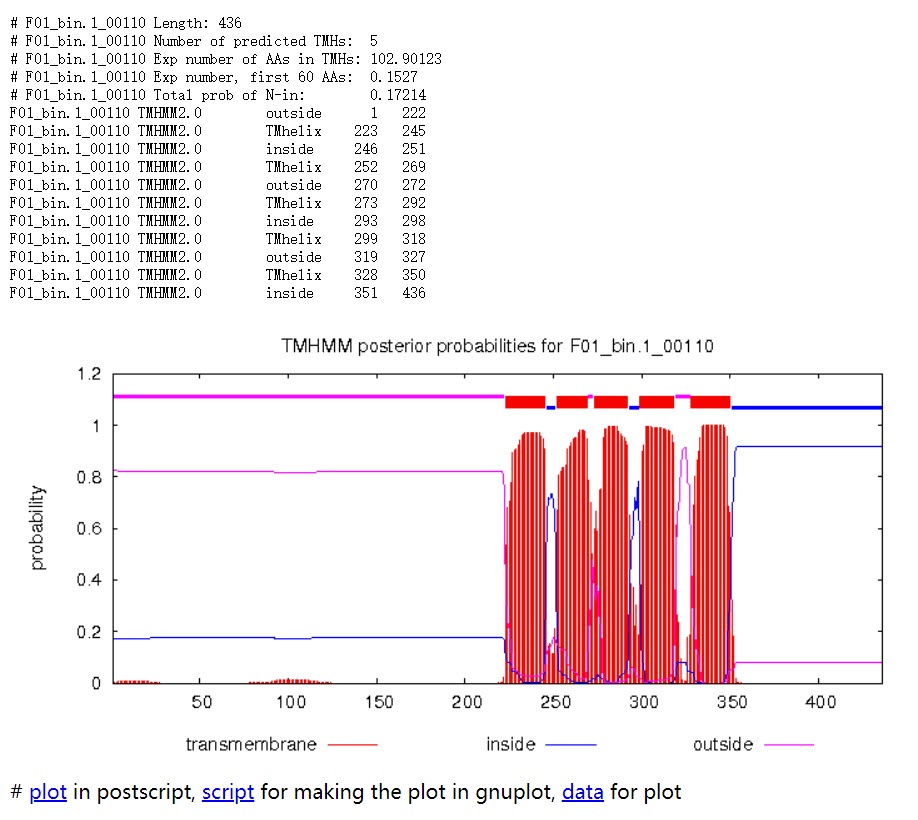
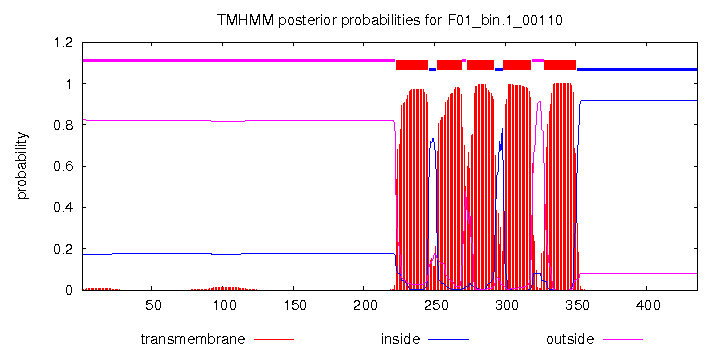
蛋白 F01_bin.1_00110 共计 436 个氨基酸,有 5 个跨膜螺旋结构。
![含有跨膜结构的蛋白]()
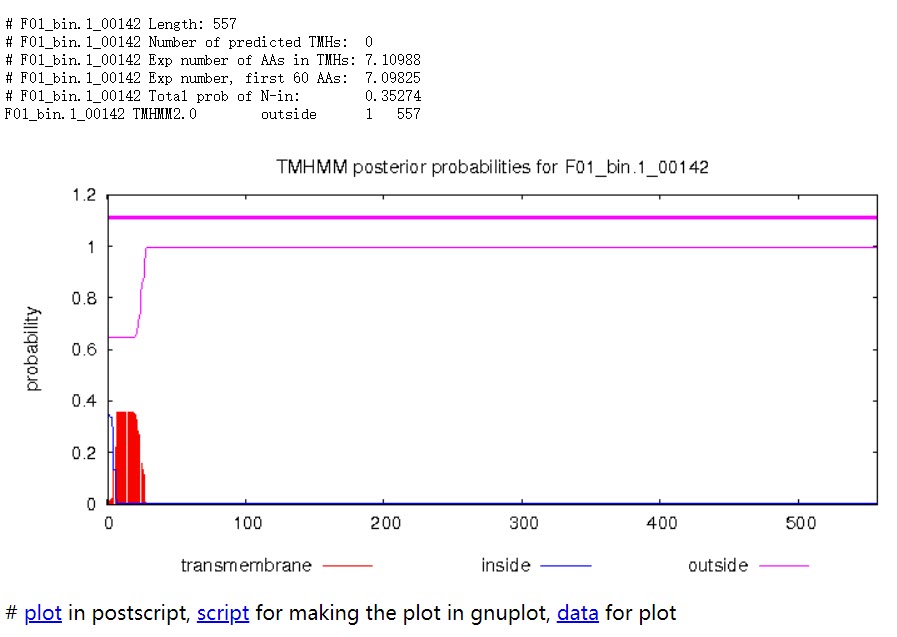
蛋白 F01_bin.1_00142 共计 557 个氨基酸,所有序列均在膜外,即该序列编码的是分泌蛋白。
![不含跨膜结构的蛋白]()
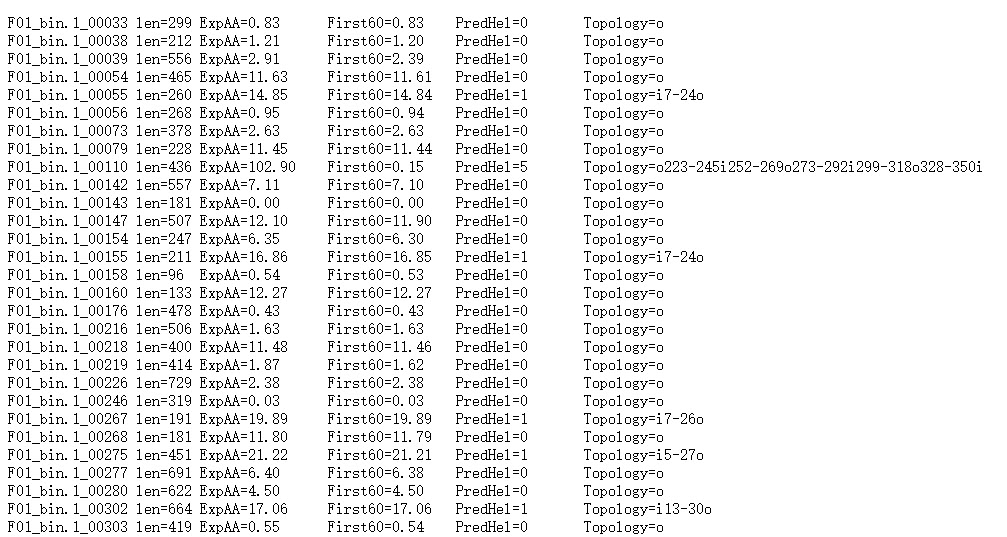
Short output format
"len=":蛋白序列的长度。
"ExpAA=":跨膜螺旋中氨基酸的预期数量。如果此数字大于 18,则很可能是跨膜蛋白(或具有信号肽)。
"First60=":在蛋白的前 60 个氨基酸中跨膜螺旋中氨基酸的预期数量。如果该数字超过几个,你应该被警告在 N 端预测的跨膜螺旋可能是一个信号肽。
"PredHel=":预测到的跨膜螺旋的数量。
"Topology=":N-best 预测的拓扑结构。拓扑是由跨膜螺旋的位置给出的,如果螺旋在内部,则由 “i” 分隔,如果螺旋在外部,则由 “o” 分隔。'i7-29o44-66i87-109o' 意味着它从膜内开始,在位置 7 到 29 有一个预测的 TMH,30-43 在膜外,然后是位置 44-66 的 TMH。
![Short output format]()
# 结果汇总
通过网页版预测我们仅得到了一个列表文件(Short output format),该文件需要自己复制网页内容粘贴到新文件中,我将其命名为*_TMHMM_SHORT.txt,并将其存放在*_signalp目录中,该目录是由 run_SignalP.pl 生成的。下面我将会统计各个基因组中信号肽蛋白的总数量、分泌蛋白数量和跨膜蛋白数量到文件 Statistics.txt 中,并分别提取每个基因组的分泌蛋白序列到*_signalp/*.secretory.faa文件中,提取跨膜蛋白序列到*_signalp/*.membrane.faa文件中。该过程将通过 tmhmm_parser.pl 完成。
#!/usr/bin/perl | |
use strict; | |
use warnings; | |
# Author: Liu Hualin | |
# Date: Oct 15, 2021 | |
open OUT, ">Statistics.txt" || die; | |
print OUT "Strain name\tSignal peptide numbers\tSecretory protein numbers\tMembrane protein numbers\n"; | |
my @sig = glob("*_signalp"); | |
foreach my $sig (@sig) { | |
$sig=~/(.+)_signalp/; | |
my $str = $1; | |
my $tmhmm = $sig . "/$str" . "_TMHMM_SHORT.txt"; | |
my $fasta = $sig . "/$str" . ".sigseq"; | |
my $secretory = $str . ".secretory.faa"; | |
my $membrane = $str . ".membrane.faa"; | |
open SEC, ">$secretory" || die; | |
open MEM, ">$membrane" || die; | |
my $out = 0; | |
my $on = 0; | |
my %hash = idseq($fasta); | |
open IN, $tmhmm || die; | |
while (<IN>) { | |
chomp; | |
$_=~s/[\r\n]+//g; | |
# print $_ . "\n"; | |
my @lines = split /\t/; | |
if ($lines[5] eq "Topology=o") { | |
$out++; | |
print SEC ">$lines[0]\n$hash{$lines[0]}\n"; | |
}else { | |
$on++; | |
print MEM ">$lines[0]\n$hash{$lines[0]}\n"; | |
} | |
} | |
close IN; | |
close SEC; | |
close MEM; | |
system("mv $secretory $membrane $sig"); | |
my $total = $out + $on; | |
print OUT "$str\t$total\t$out\t$on\n"; | |
} | |
close OUT; | |
sub idseq { | |
my ($fasta) = @_; | |
my %hash; | |
local $/ = ">"; | |
open IN, $fasta || die; | |
<IN>; | |
while (<IN>) { | |
chomp; | |
my ($header, $seq) = split (/\n/, $_, 2); | |
$header =~ /(\S+)/; | |
my $id = $1; | |
$hash{$id} = $seq; | |
} | |
close IN; | |
return (%hash); | |
} |
运行方法:将tmhmm_parser.pl放在*_signalp的上一级目录下,*_signalp目录中必须包含*_TMHMM_SHORT.txt文件和*.sigseq文件。在终端运行如下代码:
perl tmhmm_parser.pl |
# 脚本获取
关注公众号 “生信之巅”,聊天窗口回复 “c886” 获取下载链接。
 |  |
敬告:使用文中脚本请引用本文网址,请尊重本人的劳动成果,谢谢!
# 参考
SignalP V6.0
TMHMM